Identify the Stimulus for the Release of Insulin
12 Closure of K -ATP-dependent channels results in membrane depolarization and activation of voltage dependent calcium channels leading to an increase in intracellular calcium concentration. Changes in the body can be mediated by direct or indirect mechanisms.
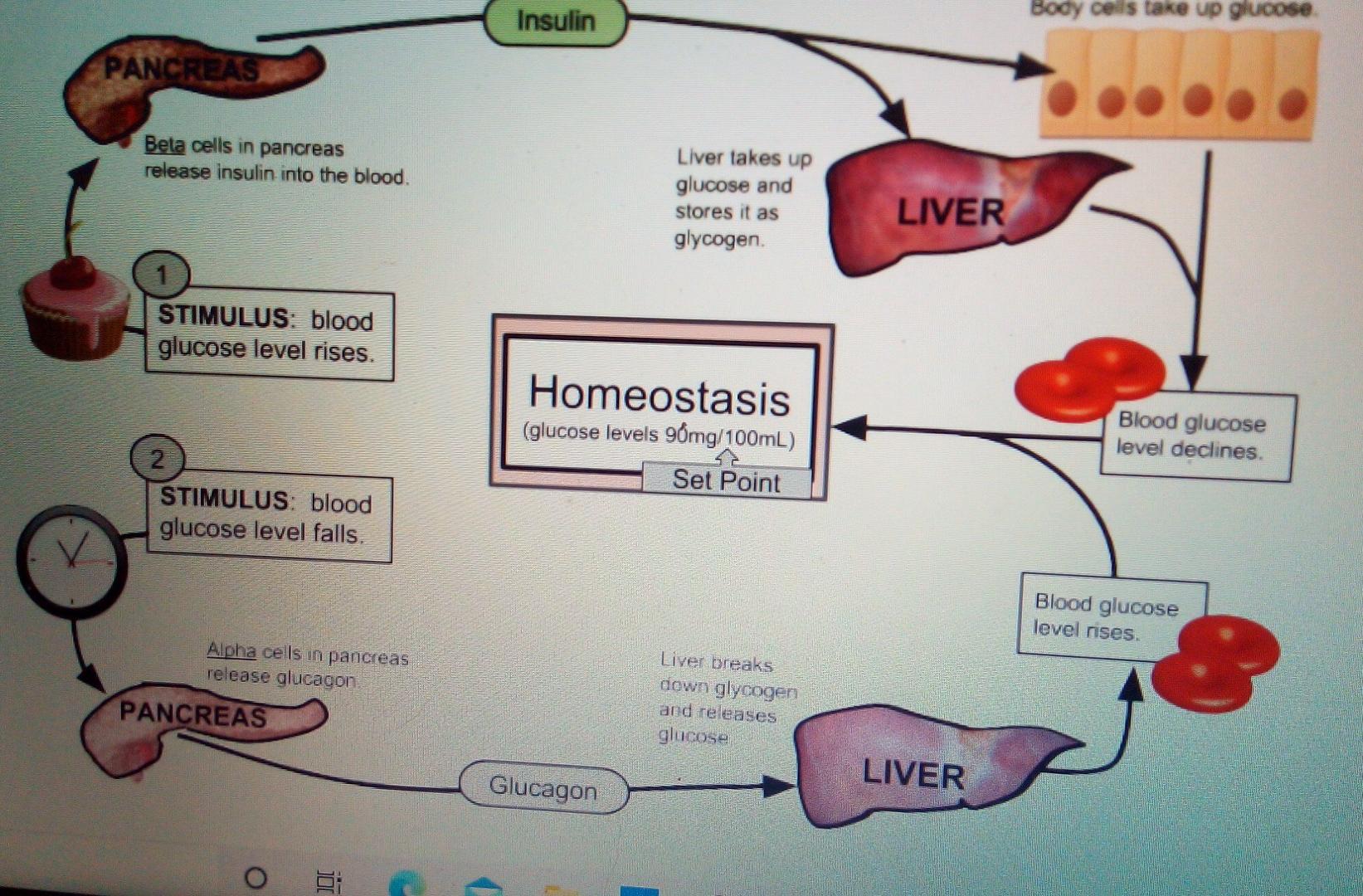
Solved Insulin Body Cells Take Up Glucose Pancreas Beta Chegg Com
Insulin is a small protein with a molecular weight of about 6000 Daltons.
. Blood pumped out of the right ventricle goes to the body OR to the lungs 3. Insulin is normally secreted by the beta cells a type of islet cell of the pancreas. Effectors- liver cells and the body cells response- decrease in blood glucose by uptake by liver cells and conversion to glycogen and uptake by body cells.
QUESTION 3 Identify the stimulus for the release of insulin. For example glucose in the blood a stimulus causes the pancreas to release insulin a reaction which in turn causes the cells to take up glucose from the blood a response. The figure to the right shows a molecular model of bovine insulin with the A.
Carbohydrate stimulates the release of insulin a hormone that transports glucose from the blood into the muscles. Identify the site of release stimulus for release and the predominant action of the following hormones. This triggers pulsatile insulin secretion.
A newly discovered hormone contains four amino acids linked together. Glucose is an effective stimulus for the release of insulin from pancreatic beta-cells but its pre-eminence for the physiological control of insulin secretion is now challenged. Parathyroid hormone thyroid hormone adrenalin insulin.
It is decreased by PTH. This amino acid is known for stimulating insulin release through electrogenic transport into the β-cell via the mCAT2A amino acid transporter resulting in membrane depolarisation a rise in intracellular Ca 2 through opening of voltage-gated Ca 2 channels and then insulin secretion. The stimulus for insulin secretion is a HIGH blood glucoseits as simple as that.
It is a protein responsible for regulating blood glucose levels as part of metabolism1 The body manufactures insulin in the pancreas and the hormone is secreted by its beta cells primarily in response to glucose1 The beta cells of the pancreas are perfectly designed fuel sensors stimulated by glucose2 As glucose levels rise in the plasma of the blood uptake. Specifically Type 1 diabetes is the inability to make. Lefèbvre in Hormonal Signaling in Biology and Medicine 2020.
Increased blood glucose levels stimulate beta cells in the pancreas to produce insulin. Glucagon increases and somatostatin decreases insulin release via paracrine actions. The blood be used by the cells.
A lowering of serum calcium is the stimulus for the endogenous release of adrenocortical hormone. Insulin triggers the uptake of glucose fatty acids and amino acids into liver adipose tissue and muscle and promotes the storage of these nutrients in the form of glycogen lipids and protein respectively. O A hypoglycemia B.
Pierre De Meyts Pierre J. It is composed of two chains held together by disulfide bonds. Identify the chemical class under which this hormone would be classified.
Sympathetic nerve stimulation inhibits insulin release. Glucose entry into the β cell is sensed by glucokinase which phosphorylates glucose to glucose-6-phosphate G6P generating ATP. The insulin response to oral glucose is much greater than the response to intravenous glucose because an intestinal factor or factors has a powerful stimulant effect on insulin secretion.
37 Control of Secretion. Inhibition of lipogenesis O inhibition of. Stimulation of glycogenesis B.
Epinephrine inhibits insulin release. What problem would be caused by not producing insulin. Can OR cannot 5.
Where must the blood go before it can be sent to the entire body. Joint and muscle pains that have no apparent cause can be a symptom of A. Insulin is a hormone released by pancreatic beta cells in response to elevated levels of nutrients in the blood.
If blood glucose levels decrease from normal which of the following changes takes place to bring glucose levels back to normal. Carbohydrate stimulates the release of insulin a hormone that transports glucose from the blood into the muscles. Epinephrine norepinephrine glucagon insulin cortisol aldosterone thyroxine growth hormone estrogen and testosterone.
The control of glucagon secretion is multifactorial and involves direct effects of nutrients on the α-cell stimulus-secretion coupling as well as paracrine regulation by insulin somatostatin and possibly other mediators such as zinc γ-amino-butyric acid GABA or. Stimulated by the release of acetylcholine by parasympathetic nerve fibers. Solutions for Chapter 5 Problem 7OQ.
Although there is always a low level of insulin secreted by the pancreas the amount secreted into the blood increases as the blood glucose rises. Neither A nor Bare correct QUESTION 4 All of the following are actions of insulin EXCEPT. The primary stimulus for insulin secretion is A.
The effects of thyroid hormones are more variable. Both A and B are correct OD. Increased exposure to sunlight.
When a person can no longer produce insulin or enough insulin they have diabetes. Transcribed image text. Insulin triggers liver muscle and fat tissue cells to absorb glucose where it is stored.
Stimulus- increase in glucose receptor- beta cells control centre- insulin sensitive cells of the hypothalamus beta cells secrete the hormone insulin. Insulin Synthesis and Secretion. 37 Arginine may also be converted to L-glutamate and thus influence insulin secretion by the.
Insulin release is stimulated by GH cortisol PRL and the gonadal steroids. Get solutions Get solutions Get solutions done loading Looking for the textbook. As glucose is absorbed blood glucose levels fall.
In the lungs the blood gives up its oxygen OR carbon dioxide and picks up oxygen OR carbon dioxide 4. Insulin is stimulated by the elevation of blood glucose levels but it is also stimulated by rising blood levels of another substance in the blood what are the substances.

Simplified Scheme Of Stimulus Secretion Coupling Pathways In The Download Scientific Diagram

Stimulus Coupling Mechanisms For Glucose Induced Insulin Secretion In Download Scientific Diagram

The Science Of Emotions How It Works Psychologicalfactsschools Emotions Medical Knowledge Physics And Mathematics
Handbook Of Diabetes 4th Edition Excerpt 4 Normal Physiology Of Insulin Secretion And Action
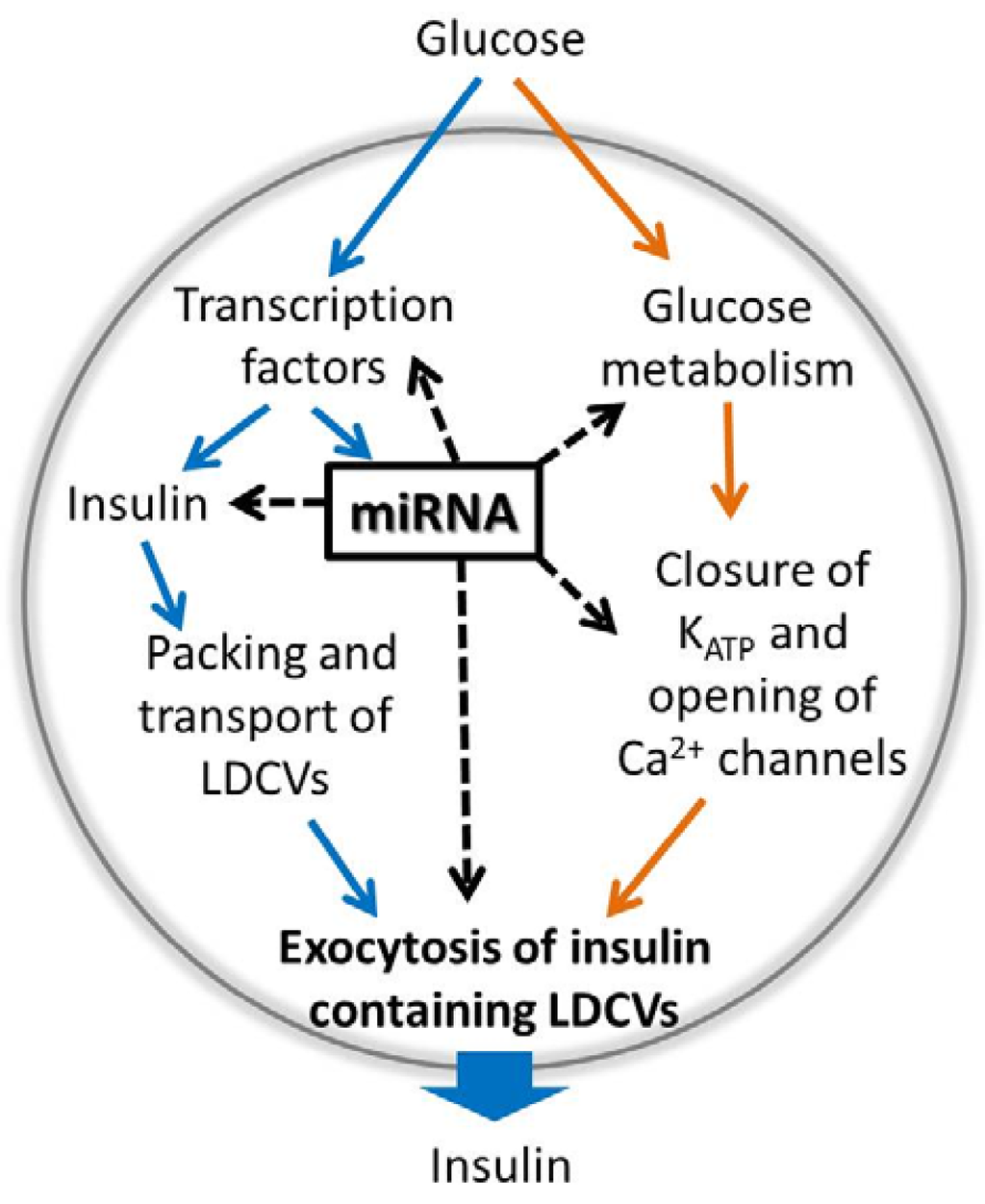
Genes Free Full Text Regulation Of Pancreatic Beta Cell Stimulus Secretion Coupling By Micrornas Html

Stimulus Secretion Coupling In The Pancreatic Cell Glut 2 Is A Download Scientific Diagram

Stimulus Secretion Coupling An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Stimulus Coupling Mechanisms For Glucose Induced Insulin Secretion In Download Scientific Diagram
Stimulus Secretion Coupling In The A Cell Low Glucose Concentration Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment